2026 How to Optimize the Aluminium Process for Maximum Efficiency?
In the pursuit of maximum efficiency in the Aluminium Process, industry leaders are continuously seeking innovative methods. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in metallurgy, "Optimizing the aluminium process is not just about speed; it's about smart integration." This statement encapsulates the essence of modern strategies in aluminium production.
Efficiency in the Aluminium Process involves various factors, such as energy consumption and production waste. Every stage offers opportunities for enhancement. A single mistake in the process can lead to significant setbacks. For many companies, this reality often means facing unexpected challenges. Reflecting on these hurdles reveals that the quest for perfection is ongoing.
Moreover, the technological advancements in the Aluminium Process are both exciting and daunting. While automation can streamline tasks, it also raises questions about workforce dynamics. The balance between technology and human skill is delicate. Organizations must evaluate how to evolve without losing sight of their core principles. Embracing this complexity might lead to breakthroughs in achieving true efficiency.

Understanding the Aluminium Production Process and Its Challenges
The aluminium production process is intricate and faces various challenges. Primary production involves extracting aluminium from its ore, bauxite. This process is energy-intensive, consuming about 15,000 kWh per ton of aluminium produced, according to the International Aluminium Institute. This high energy demand escalates operational costs and impacts sustainability efforts.
Recycling aluminium presents a viable solution. Recycled aluminium requires only 5% of the energy compared to primary production. However, the purity of recycled materials can be a concern. Impurities can lead to defects in the final product. The industry must focus on refining recycling techniques to ensure high-quality outputs.
Tips for enhancing efficiency include investing in automation. Automated systems can streamline operations, reducing human error and increasing productivity. Regular maintenance of equipment is vital to prevent breakdowns that can halt production. Training staff on best practices is equally important. Knowledgeable workers can identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements. Embracing these strategies can lead to significant advancements in the aluminium production sector.
Key Factors Influencing Aluminium Processing Efficiency
When optimizing aluminium processing, several key factors come into play. One primary aspect is temperature control. Maintaining the right temperature is crucial. Too high or too low can lead to defects. A small error in temperature can result in a significant waste of resources. Monitoring this closely is essential for efficiency.
Another influencing factor is tooling and machinery. Well-maintained tools increase precision and reduce downtime. However, many operations overlook regular servicing. This negligence can lead to unexpected breakdowns. That’s a reflection point for many manufacturers. They need to balance cost and maintenance.
Lastly, workforce training plays a vital role in efficiency. Skilled operators make fewer mistakes. They can also suggest improvements based on their experiences. Yet, often, training is not prioritized. Investing in continuous education can yield substantial long-term benefits. Finding the right balance in these areas can transform processing efficiency dramatically.
2026 How to Optimize the Aluminium Process for Maximum Efficiency? - Key Factors Influencing Aluminium Processing Efficiency
| Factor | Description | Impact on Efficiency (%) | Improvement Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Quality | The purity and quality of aluminum used directly affects processing outcomes. | 15% | Source high-quality materials; perform regular quality checks. |
| Process Temperature | Optimal temperature settings enhance material flow and reduce defects. | 20% | Implement advanced temperature control systems; monitor continuously. |
| Machinery Maintenance | Regular maintenance prevents breakdowns and ensures consistent operation. | 10% | Establish a routine maintenance schedule; train staff for basic repairs. |
| Operator Training | Skilled operators can significantly reduce errors and optimize settings. | 12% | Conduct regular training sessions; incorporate best practices. |
| Production Scheduling | Efficient scheduling reduces downtime and improves workflow efficiency. | 18% | Use software tools for optimal scheduling; align resources accordingly. |
Innovative Technologies for Enhanced Aluminium Processing
Innovative technologies are transforming aluminium processing into a more efficient and sustainable practice. Automation is one of these key advancements. Robots now handle repetitive tasks, reducing human error and increasing speed. For instance, automated systems can sort and package raw materials faster than ever. This efficiency also translates to lower operational costs.
Another fascinating technology is advanced melting methods. Induction melting offers better energy control, which minimizes waste. This technique reduces the amount of energy needed to melt aluminium significantly. Thermodynamic innovations are also making recycling processes more efficient. They allow for better separation of materials, ensuring higher purity in recycled aluminium.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Not all facilities can adopt these technologies due to high initial costs. Also, the rapid pace of innovation can outstrip the workforce’s skill levels. Training becomes crucial but often lags behind the implementation of new technologies. These are areas that need ongoing reflection and improvement for the industry to thrive.
Best Practices for Waste Reduction in Aluminium Production
In aluminium production, waste reduction is vital. Every step in the process generates by-products. These can be valuable if managed properly. Recycling scrap material is one effective method. Collecting and reprocessing scrap reduces the need for virgin materials. It conserves resources and minimizes energy consumption.
Energy efficiency is another key factor. Optimizing furnace temperatures can decrease emissions. However, many facilities struggle to maintain consistent temperatures. Frequent fluctuations can lead to increased waste and inefficiencies. Regular monitoring is necessary. Investing in better temperature controls might seem costly but pays off in the long run.
Employees play a crucial role in waste reduction efforts. Training programs on best practices can improve awareness. Yet, some workers may resist change. They might feel overwhelmed by new procedures. Open communication can ease these transitions. Listening to feedback encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Making small adjustments can lead to significant savings over time.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement in Aluminium Manufacturing
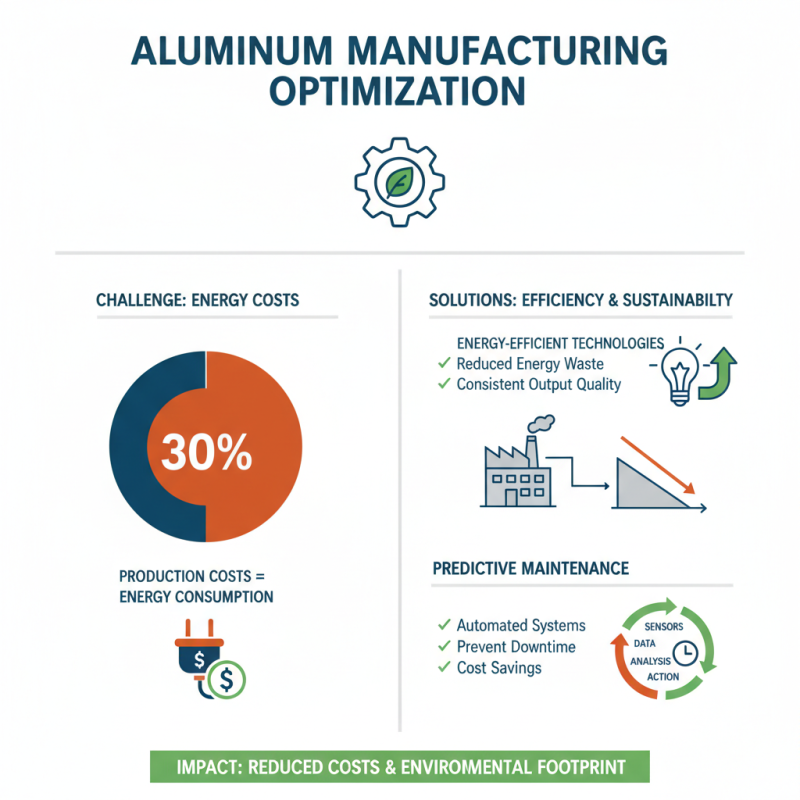
Optimizing the aluminium manufacturing process can vastly improve efficiency and sustainability. According to industry reports, about 30% of production costs in aluminium manufacturing stem from energy consumption. Therefore, implementing energy-efficient technologies is crucial. Techniques like automated process control can reduce energy waste while maintaining output quality. Automated systems can also enhance predictive maintenance, which is essential to prevent costly downtimes.
Continuous improvement must focus on raw material usage. Studies reveal that reducing scrap rates can save up to 20% of material costs. Adjusting melter charging practices and improving operator training can significantly minimize waste. However, achieving these goals requires a culture of accountability. Employees must understand their role in waste reduction, often leading to greater engagement and ownership.
Innovation in recycling processes also plays a vital role. With over 75% of aluminium ever produced still in use, enhancing recycling efficiency is crucial. Yet, many facilities struggle with outdated sorting technologies. Investing in advanced sorting equipment may seem expensive upfront but can yield substantial long-term savings. It is vital to regularly assess equipment and processes for improvements. Constant reflection on current practices can uncover hidden inefficiencies.
Related Posts
-

2026 Top Aluminium Profile For Doors And Windows Trends to Watch?
-

How to Choose the Best Aluminium Profile for Doors and Windows Installation
-

Ultimate Guide to Aluminium Profile Cladding Tips for Effective Installation
-
Top 10 Benefits of Choosing Aluminium Windows in Turkey for Your Home
-

How to Choose Aluminium Profile Wall Cladding for Your Project?